What is Redis?
Redis Server is an In-Memory Database system designed for fast and efficient data storage and management. Redis is essentially a Key-Value Store, and its operation is similar to NoSQL databases. This service can store data in RAM for extremely fast access.
Redis was initially developed by Salvatore Sanfilippo and has become one of the most important tools in Scalable Systems design today.
Why is Redis Popular?
One of the main reasons for Redis’s popularity is its high speed in data processing. Since Redis stores data in memory (unlike traditional databases that store data on disk), read and write operations are much faster.
In addition, Redis provides features such as Persistence, Replication, and support for complex data structures. Therefore, Redis is not just a simple caching system, but a versatile tool for managing data at scale.
Key Features of Redis Server
Redis has a set of unique features that distinguish it from other similar databases:
- In-Memory Storage
All data is stored in RAM, which results in very high access speeds. - Diverse Data Structures
Redis supports various data structures such as Strings, Lists, Sets, Hashes, and Sorted Sets. This makes it suitable for various scenarios. - Data Persistence
Unlike many caching systems, Redis also allows data to be stored on disk, so that data is not lost when the server is restarted. - Data Replication
Redis supports Master-Slave Replication, which increases High Availability and improves workload distribution. - Pub/Sub Support
Redis has Publish/Subscribe capability that can be used to design Real-Time systems such as chats, Notifications, or Streams.
Redis allows you to use the Lua language to write server-side scripts for optimized execution of more complex operations.
How Does Redis Work?
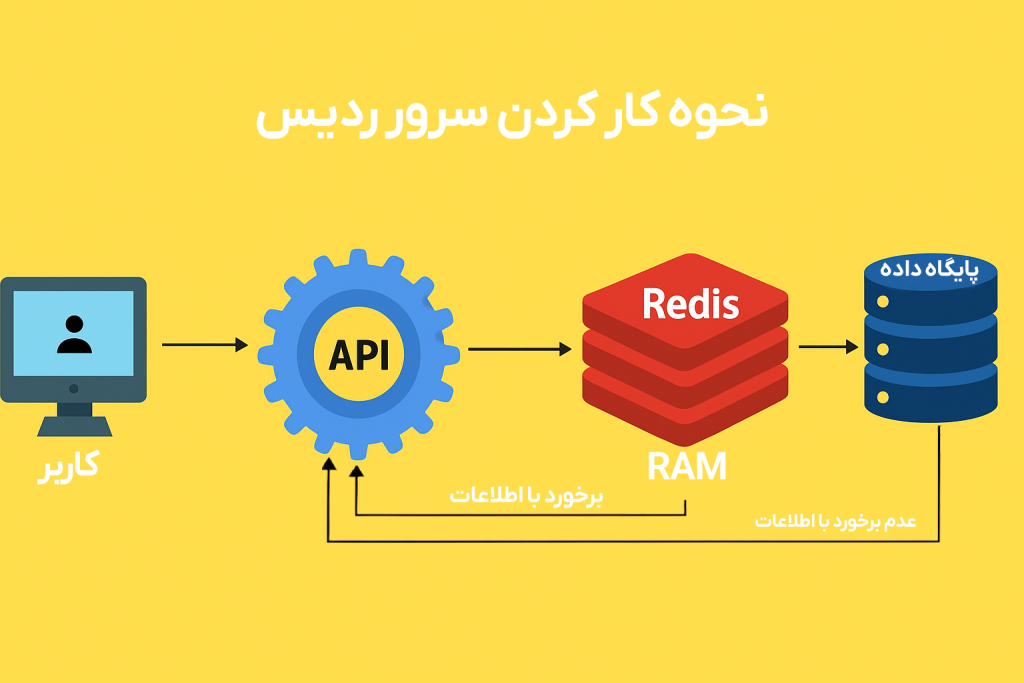
Redis follows the Client-Server model. In this model, the Client sends its commands to the Redis Server via the TCP protocol and receives the response immediately.
In simpler terms:
- The client (e.g., a web application) sends a request to store or retrieve data.
- Redis stores that data in RAM.
- If needed, Redis returns the information due to a Cache Hit.
- If the information is not available in RAM and a Cache Miss occurs, Redis retrieves the information from the main database.
Applications of Redis in System Design
Redis is used in various scenarios in modern system architecture:
- Caching System
Redis is often used to temporarily store data and reduce pressure on the main database. For example, on high-traffic websites, query results are stored in Redis. - Session Management
Many applications (especially web services) use Redis to store user sessions. - Message Queues
Redis can act as a Message Queue using Lists or Streams. - Counting Systems
With Atomic Increment capability, Redis can be used to count visits, likes, or real-time statistics. - Leaderboards and Scoring
The Sorted Set structure in Redis is ideally suited for ranking users in games or applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Redis
Advantages:
- Very high speed due to in-memory storage.
- Support for diverse data structures.
- Suitable for Real-Time systems.
- Scalability using Replication and Clustering.
Disadvantages:
- Due to storing data in RAM, memory costs may increase in large systems.
- If Persistence is not configured, data may be lost after a Restart.
Redis Server is one of the fastest and most popular In-Memory databases, holding a special place in the architecture of modern systems. With its powerful data structures and very high speed, Redis is an excellent option for implementing caching systems, session management, message queues, and even real-time analytics.
If you are looking for a lightweight, fast, and flexible solution for data management, Redis can be one of the best choices for your project’s infrastructure.
